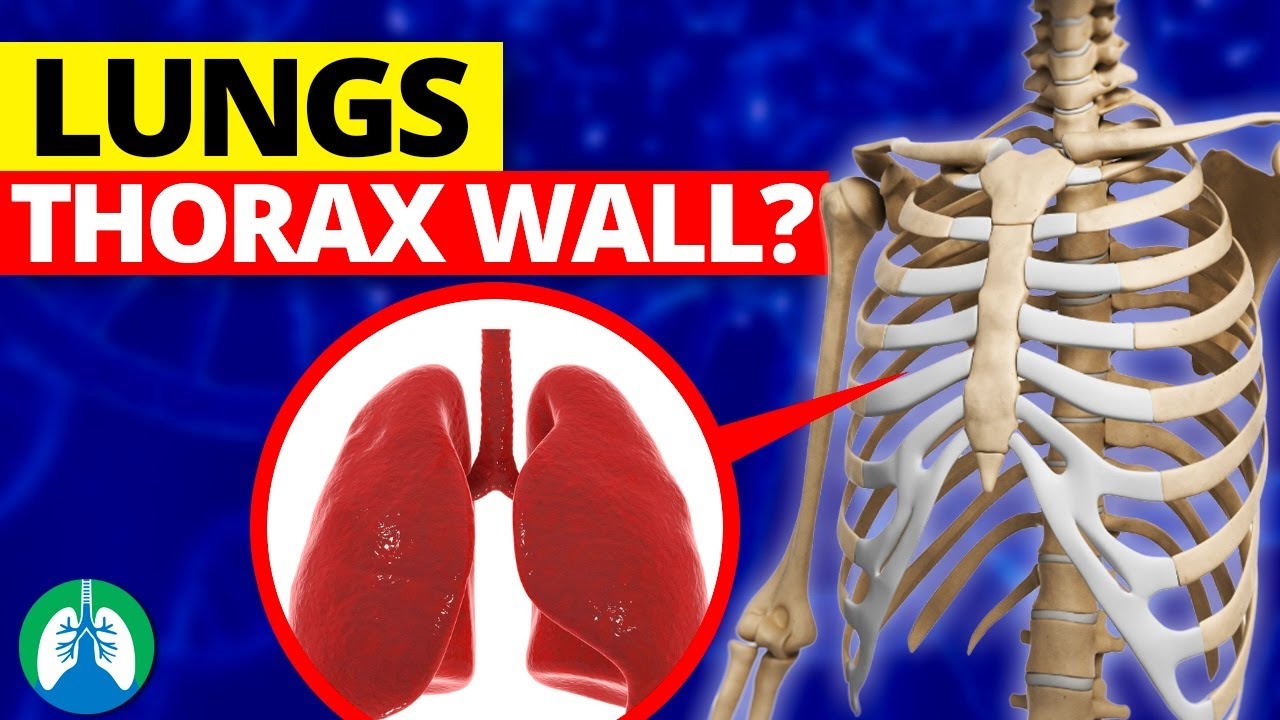
The lungs are held to the thorax wall by a thin, double-layered membrane called the pleura. The inner layer, known as the visceral pleura, is attached directly to the lung tissue while the outer layer, called the parietal pleura, is attached to the inner surface of the thorax wall. These two layers are separated by a small amount of fluid, known as pleural fluid, which helps to reduce friction and allows for smooth movement of the lungs during breathing. The pleura not only holds the lungs in place within the thorax, but also helps to maintain the shape of the lungs and facilitate the exchange of gases during respiration.