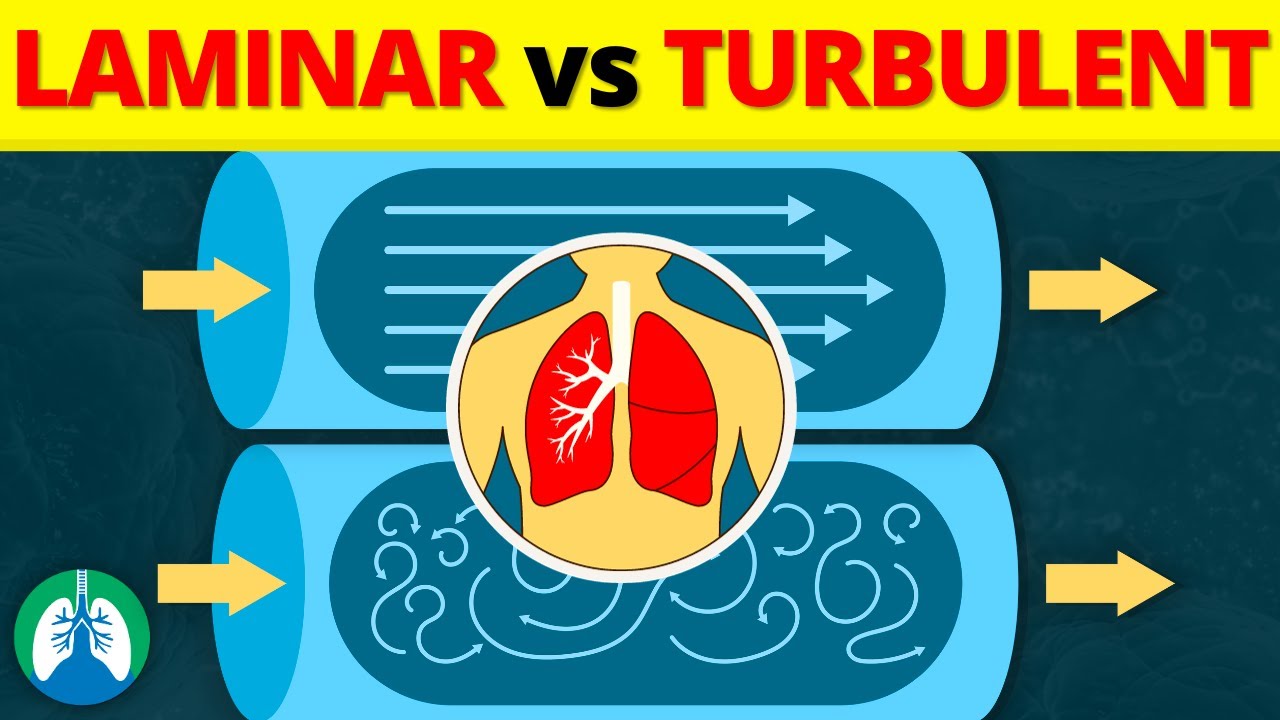
In the lungs, air flow can be categorized as either laminar or turbulent. Laminar flow occurs when air moves smoothly and in parallel layers, with minimal disruption or mixing. This type of flow is more efficient and allows for optimal gas exchange in the alveoli. On the other hand, turbulent flow is characterized by chaotic, swirling motion of air particles, which can lead to increased resistance and energy loss. Turbulent flow is more likely to occur in areas of the lungs with high velocity, such as during forced expiration or in obstructed airways. Overall, maintaining laminar flow in the lungs is crucial for efficient gas exchange and optimal respiratory function.